RNA velocity with kallisto | bus and velocyto.R
Lambda Moses
2020-02-07
Last updated: 2020-02-07
Checks: 7 0
Knit directory: BUSpaRse_notebooks/
This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr (version 1.6.0). The Checks tab describes the reproducibility checks that were applied when the results were created. The Past versions tab lists the development history.
Great! Since the R Markdown file has been committed to the Git repository, you know the exact version of the code that produced these results.
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
The command set.seed(20181214) was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible.
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
Nice! There were no cached chunks for this analysis, so you can be confident that you successfully produced the results during this run.
Great job! Using relative paths to the files within your workflowr project makes it easier to run your code on other machines.
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility. The version displayed above was the version of the Git repository at the time these results were generated.
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can use wflow_publish or wflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Ignored files:
Ignored: .Rhistory
Ignored: .Rproj.user/
Ignored: BUSpaRse_notebooks.Rproj
Ignored: MouseMineSynteny.blocks.gz
Ignored: NCBI_Human_forSynteny.gff3.gz
Ignored: data/fastqs/
Ignored: data/hgmm_100_fastqs.tar
Ignored: data/hgmm_1k_fastqs.tar
Ignored: data/hgmm_1k_v3_fastqs.tar
Ignored: data/hgmm_1k_v3_fastqs/
Ignored: data/hs_cdna.fa.gz
Ignored: data/hs_cdna96.fa.gz
Ignored: data/mm_cdna.fa.gz
Ignored: data/mm_cdna96.fa.gz
Ignored: data/mm_cdna97.fa.gz
Ignored: data/neuron_10k_v3_fastqs.tar
Ignored: data/neuron_10k_v3_fastqs/
Ignored: data/retina/
Ignored: data/whitelist_v2.txt
Ignored: data/whitelist_v3.txt
Ignored: output/hs_mm_tr_index.idx
Ignored: output/hs_mm_tr_index96.idx
Ignored: output/mm_cDNA_introns_97.idx
Ignored: output/mm_cDNA_introns_97_collapse.idx
Ignored: output/mm_tr_index.idx
Ignored: output/mm_tr_index97.idx
Ignored: output/out_hgmm1k2/
Ignored: output/out_hgmm1k_v3/
Ignored: output/out_retina/
Ignored: tmp/
Untracked files:
Untracked: .ipynb_checkpoints/
Untracked: SRR7244429_1.fastq
Untracked: SRR7244429_2.fastq
Untracked: analysis/dropseq_retina.Rmd
Untracked: analysis/ee_ie_junctions.Rmd
Untracked: analysis/junction.Rmd
Untracked: analysis/junction2.Rmd
Untracked: human_mouse_transcript_to_gene.tsv
Untracked: output/ee_ie/
Untracked: output/neuron10k/
Untracked: output/neuron10k_collapse/
Untracked: output/neuron10k_junction/
Untracked: output/neuron10k_velocity/
Untracked: output/out_hgmm1k/
Untracked: output/tr2g_hgmm.tsv
Untracked: output/tr2g_mm97.tsv
Untracked: problem5.ipynb
Untracked: test/
Unstaged changes:
Modified: analysis/monocle2.Rmd
Deleted: colab/.ipynb_checkpoints/10xv3-checkpoint.ipynb
Deleted: colab/.ipynb_checkpoints/Monocle 2-checkpoint.ipynb
Deleted: colab/.ipynb_checkpoints/Slingshot-checkpoint.ipynb
Deleted: colab/10xv3.ipynb
Deleted: colab/Mixed species (10x v2 chemistry).ipynb
Deleted: colab/Monocle 2.ipynb
Deleted: colab/Slingshot.ipynb
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.
These are the previous versions of the R Markdown and HTML files. If you’ve configured a remote Git repository (see ?wflow_git_remote), click on the hyperlinks in the table below to view them.
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rmd | a9f8930 | Lambda Moses | 2020-02-07 | Don’t show SCTransform warnings |
| html | 3655e91 | Lambda Moses | 2020-02-07 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 26a6c1b | Lambda Moses | 2020-02-07 | Updated SingleR section |
| html | 154f762 | Lambda Moses | 2020-01-18 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 5526f5a | Lambda Moses | 2020-01-18 | OK, we do need a different index and bus file for velocity and just gene count |
| html | db44e2e | Lambda Moses | 2020-01-18 | Build site. |
| Rmd | da56d19 | Lambda Moses | 2020-01-18 | Updated wording to reflect that SingleR is on Bioconductor. |
| html | 39e7b2b | Lambda Moses | 2019-09-13 | Build site. |
| Rmd | be4469c | Lambda Moses | 2019-09-13 | Keep isoforms separate, also label clusters on velocity plots |
| html | 5159d4a | Lambda Moses | 2019-09-06 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 0546e85 | Lambda Moses | 2019-09-06 | Updated for the new version of BUSpaRse |
| html | cba7dc4 | Lambda Moses | 2019-08-27 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 3312497 | Lambda Moses | 2019-08-27 | To be consistent with velocyto |
| html | 9b05bd3 | Lambda Moses | 2019-08-21 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 1a1b473 | Lambda Moses | 2019-08-21 | Forgot to update a paragraph explaining bash code |
| html | 84f0381 | Lambda Moses | 2019-08-21 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 85be0ed | Lambda Moses | 2019-08-21 | Updated for bustools 0.39.3 and newer development version of Seurat |
| html | c3fe4dc | Lambda Moses | 2019-07-25 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 9904300 | Lambda Moses | 2019-07-25 | Stuff users won’t see, but saves me time |
| html | e0ec72a | Lambda Moses | 2019-07-25 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 54e66d4 | Lambda Moses | 2019-07-25 | Added phase portraits and fixed some embarrasingly wrong bash chunks. |
| Rmd | 342b3bf | Lambda Moses | 2019-07-25 | Reran with Ensembl 97, fixed embarrasingly wrong bash chunks, and added phase portraits |
| html | a3abb12 | Lambda Moses | 2019-07-24 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 28b6ed4 | Lambda Moses | 2019-07-24 | Changed the embarrasing title |
| html | 22204f9 | Lambda Moses | 2019-07-24 | Build site. |
| Rmd | 1bd5af5 | Lambda Moses | 2019-07-24 | RNA velocity tutorial |
In this notebook, we perform RNA velocity analysis on the 10x 10k neurons from an E18 mouse. Instead of the velocyto command line tool, we will use the kallisto | bus pipeline, which is much faster than velocyto, to quantify spliced and unspliced transcripts.
Setup
If you would like to rerun this notebook, you can git clone this repository or directly download this notebook from GitHub.
Install packages
This notebook demonstrates the use of command line tools kallisto and bustools. Please use kallisto >= 0.46, whose binary can be downloaded here. Also, please use bustools >= 0.39.3, whose binary of bustools can be found here. User interface of bustools has changed in version 0.39.3. For version 0.39.2, see earlier git commits of this notebook.
After you download the binary, you should decompress the file (if it is tar.gz) with tar -xzvf file.tar.gz in the bash terminal, and add the directory containing the binary to PATH by export PATH=$PATH:/foo/bar, where /foo/bar is the directory of interest. Then you can directly invoke the binary on the command line as we will do in this notebook.
We will be using the R packages below. BUSpaRse is now on Bioconductor 3.10 (development version of Bioconductor). For Mac users, see the installation note for BUSpaRse. BUSpaRse will be used to generate the transcript to gene file for bustools and to read output of bustools into R. We will also use Seurat version 3 which is now on CRAN. Recently, Satija lab announced SeuratWrappers, with which we can run RNA velocity directly from Seurat. SeuratWrappers is also GitHub only at present. We need to install velocyto.R, which is GitHub only, to compute and visualize RNA velocity after quantifying spliced and unspliced transcripts.
# Install devtools if it's not already installed
if (!require(devtools)) {
install.packages("devtools")
}
# Install from GitHub
devtools::install_github("BUStools/BUSpaRse")
devtools::install_github("satijalab/seurat-wrappers")
devtools::install_github("velocyto-team/velocyto.R")This vignette uses the version of DropletUtils from Bioconductor version 3.10; the version from Bioconductor 3.8 has a different user interface. If you are using a version of R older than 3.6.0 and want to rerun this vignette, then you can adapt the knee plot code to the older version of DropletUtils, or install DropletUtils from GitHub, which I did for this notebook. BSgenome.Mmusculus.UCSC.mm10, AnnotationHub, SingleR are also on Bioconductor. Bioconductor packages can be installed as such:
if (!require(BiocManager)) {
install.packages("BiocManager")
}
BiocManager::install(c("DropletUtils", "BSgenome.Mmusculus.UCSC.mm10",
"AnnotationHub", "SingleR"))The other packages are on CRAN.
library(BUSpaRse)
library(Seurat)
library(SeuratWrappers)
library(BSgenome.Mmusculus.UCSC.mm10)
library(AnnotationHub)
library(zeallot) # For %<-% that unpacks lists in the Python manner
library(DropletUtils)
library(tidyverse)
library(GGally) # For ggpairs
library(velocyto.R)
library(SingleR)
library(scales)
library(plotly)
theme_set(theme_bw())Download data
The dataset we are using is 10x 10k neurons from an E18 mouse (almost 25 GB).
# Download data
if (!file.exists("./data/neuron_10k_v3_fastqs.tar")) {
download.file("http://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/10x.files/samples/cell-exp/3.0.0/neuron_10k_v3/neuron_10k_v3_fastqs.tar", "./data/neuron_10k_v3_fastqs.tar", method = "wget", quiet = TRUE)
}Then untar the downloaded file.
cd ./data
tar -xvf ./neuron_10k_v3_fastqs.tarGenerate spliced and unspliced matrices
In order to know which reads come from spliced as opposed to unspliced transcripts, we need to see whether the reads contain intronic sequences. Thus we need to include intronic sequences in the kallisto index. This can be done with the BUSpaRse function get_velocity_files, which generates all files required to run RNA velocity with kallisto | bustools. First, we need a genome annotation to get intronic sequences. We can get genome annotation from GTF or GFF3 files from Ensembl with getGTF or getGFF from the R package biomartr, but Bioconductor provides genome annotations in its databases and package ecosystem as well. UCSC annotation can be obtained from Bioconductor package TxDb.Mmusculus.UCSC.mm10.knownGene. Here Ensembl version 97 is used, but Bioconductor 3.10 also provides version 98.
# query AnnotationHub for mouse Ensembl annotation
ah <- AnnotationHub()snapshotDate(): 2019-10-29query(ah, pattern = c("Ensembl", "97", "Mus musculus", "EnsDb"))AnnotationHub with 1 record
# snapshotDate(): 2019-10-29
# names(): AH73905
# $dataprovider: Ensembl
# $species: Mus musculus
# $rdataclass: EnsDb
# $rdatadateadded: 2019-05-02
# $title: Ensembl 97 EnsDb for Mus musculus
# $description: Gene and protein annotations for Mus musculus based on Ensem...
# $taxonomyid: 10090
# $genome: GRCm38
# $sourcetype: ensembl
# $sourceurl: http://www.ensembl.org
# $sourcesize: NA
# $tags: c("97", "AHEnsDbs", "Annotation", "EnsDb", "Ensembl", "Gene",
# "Protein", "Transcript")
# retrieve record with 'object[["AH73905"]]' # Get mouse Ensembl 97 annotation
edb <- ah[["AH73905"]]loading from cacherequire("ensembldb")Explaining the arguments of get_velocity_files:
X, the genome annotation, which is hereedb. Hereedbis anEnsDbobject. Other allowed inputs are: a path to a GTF file, aGRangesobject made from loading a GTF file into R, or aTxDbobject (e.g.TxDb.Mmusculus.UCSC.mm10.knownGene).L: Length of the biological read of the technology of interest. For 10x v1 and v2 chemistry,Lis 98 nt, and for v3 chemistry,Lis 91 nt. The length of flanking region around introns isL-1, to capture reads from nascent transcripts that partially map to intronic and exonic sequences.Genome: Genome, either aDNAStringSetorBSgenomeobject. Genomes of Homo sapiens and common model organisms can also be easily obtained from Bioconductor. The one used in this notebook is from the packageBSgenome.Mmusculus.UCSC.mm10. Alternatively, you can download genomes from Ensembl, RefSeq, or GenBank withbiomartr::getGenome. Make sure that the annotation and the genome use the same genome version, which is here GRCm38 (mm10).Transcriptome: While you may supply a transcriptome in the form of a path to a fasta file or aDNAStringSet, this is not required. The transcriptome can be extracted from the genome with the gene annotation. We recommend extracting the transcriptome from the genome, so the transcript IDs used in the transcriptome and the annotation (and importantly, in thetr2g.tsvfile, explained later) are guaranteed to match. In this notebook, the transcriptome is not supplied and will be extracted from the genome.isoform_action: There are two options regarding gene isoforms from alternative splicing or alternative transcription start or termination site. One is to get intronic sequences separately for each isoform, and another is to collapse all isoforms of a gene by taking the union of all exonic ranges of the gene. To be honest, I implemented both options since I wasn’t sure which one is better. Now I reason that keeping isoforms separate is better, since given the way reads are assigned to “spliced” or “unspliced”, reads that are ambiguous due to alternative splicing will be discarded anyway and collapsing isoforms will inflate the counts in the spliced gene count matrices. Earlier versions of this notebook did collapse isoforms, so you can look at the previous version to compare results.
get_velocity_files(edb, L = 91, Genome = BSgenome.Mmusculus.UCSC.mm10,
out_path = "./output/neuron10k_velocity",
isoform_action = "separate")For regular gene count data, we build a kallisto index for cDNAs as reads are pseudoaligned to cDNAs. Here, for RNA velocity, as reads are pseudoaligned to the flanked intronic sequences in addition to the cDNAs, the flanked intronic sequences should also be part of the kallisto index. We advise you to run this step on a server, as it takes up to about 50 GB of memory and takes about an hour to run.
# Intron index
kallisto index -i ./output/mm_cDNA_introns_97.idx ./output/neuron10k_velocity/cDNA_introns.faUsing the kb wrapper
With kallisto and bustools, it takes several commands to go from fastq files to the spliced and unspliced matrices, which is quite cumbersome. So a wrapper called kb was written to condense those steps to one. The command line tool kb can be installed with
pip install kb-pythonThen we can use the following command to generate the spliced and unspliced matrices:
cd ./output/neuron10k_velocity
kb count -i ../mm_cDNA_introns_97.idx -g tr2g.tsv -x 10xv3 -o kb \
-c1 cDNA_tx_to_capture.txt -c2 introns_tx_to_capture.txt --lamanno \
../../data/neuron_10k_v3_fastqs/neuron_10k_v3_S1_L002_R1_001.fastq.gz \
../../data/neuron_10k_v3_fastqs/neuron_10k_v3_S1_L002_R2_001.fastq.gz \
../../data/neuron_10k_v3_fastqs/neuron_10k_v3_S1_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz \
../../data/neuron_10k_v3_fastqs/neuron_10k_v3_S1_L001_R2_001.fastq.gzThe mtx files are in the counts_unfiltered directory.
Read the next section for instructions of going from fastq files to the matrices directly with kallisto and bustools. This is helpful to modularize the workflow. The matrices used in this notebook were generated in the next section.
Directly using kallisto and bustools
The initial bus file is generated the same way as in regular gene count data, except with the cDNA + flanked intron index.
cd ./data/neuron_10k_v3_fastqs
kallisto bus -i ../../output/mm_cDNA_introns_97.idx \
-o ../../output/neuron10k_velocity -x 10xv3 -t8 \
neuron_10k_v3_S1_L002_R1_001.fastq.gz neuron_10k_v3_S1_L002_R2_001.fastq.gz \
neuron_10k_v3_S1_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz neuron_10k_v3_S1_L001_R2_001.fastq.gzThe most recent version of BUSpaRse ensures that all transcripts on the capture list are present in the transcriptome. Otherwise the output of bustools capture will be wrong. I hope that this will be fixed soon or will get a helpful error message.
A barcode whitelist of all valid barcode can be used, though is not strictly required. The 10x whitelist contains all barcodes from the kit. The 10x whitelist file comes with Cell Ranger installation, and is copies to the working directory of this notebook. For bustools, the whitelist must be a text file with one column, each row of which is a valid cell barcode. The text file must not be compressed. If you do not have a whitelist, the most recent version of bustools can generate one based on data. The bustools whitelist command can also remove barcodes with too few reads, which means removing what may be empty droplets.
cp ~/cellranger-3.0.2/cellranger-cs/3.0.2/lib/python/cellranger/barcodes/3M-february-2018.txt.gz \
./data/whitelist_v3.txt.gz
# Decompress
gunzip ./data/whitelist_v3.txt.gzThe bustools correct command checks the whitelist and can correct some barcodes not on the whitelist but might have been due to sequencing error or mutation. If you do not wish to use a whitelist, then you can skip bustools correct below and go straight to bustools sort. In bash, | is a pipe just like the magrittr pipe %>% in R. The - by the end of the bustools sort command indicates where what goes through the pipe goes, i.e. the output of bustools correct is becoming the input to bustools sort. -t4 means using 4 threads.
The bustools capture command determines what is from cDNA and what is from the flanked introns and generate two separate bus files. The -s flag specifies that transcripts are to be captured; bustools capture also supports barcodes (-b) and UMIs (-u). To be consistent with velocyto, here “spliced” reads are those not mapping to any flanked intronic regions (so can’t be spanning intron-exon junctions), and “unspliced” reads are those not mapping to any exclusively exonic regions. The -x flag is used to find the complement of the capture list (which is the argument to -c), so the complement to the intronic list gives us the “spliced” reads from the above criterion, and the complement to the exonic list gives us the “unspliced” reads from the above criterion. This operates at the read or bus record level rather than the UMI or transcript level; the first bustools capture command (for spliced matrix) only cares whether a UMI for a barcode has a read that only maps to exonic sequences, counting it as spliced, but the command does not care if that same UMI has another read that only maps to intronic sequences, which is evidence that the transcript represented by that UMI is actually not fully spliced. That’s why I think this method counts some transcripts that in fact have intronic sequences as spliced, thus inflating the counts in the spliced matrix. Transcripts that are not fully spliced – whether nascent transcripts or transcripts with retained introns – do still have exons and even exon-exon junctions, as splicing is concurrent with transcriptions and usually not all introns are retained.
cd ./output/neuron10k_velocity
bustools correct -w ../../data/whitelist_v3.txt -p output.bus | \
bustools sort -o output.correct.sort.bus -t4 -
bustools capture -s -x -o spliced.bus -c ./introns_tx_to_capture.txt -e matrix.ec -t transcripts.txt output.correct.sort.bus
bustools capture -s -x -o unspliced.bus -c ./cDNA_tx_to_capture.txt -e matrix.ec -t transcripts.txt output.correct.sort.busUnlike for just a gene count matrix, for RNA velocity, 2 matrices are generated. One for spliced transcripts, and the other for unspliced.
cd ./output/neuron10k_velocity
bustools count -o unspliced -g ./tr2g.tsv -e matrix.ec -t transcripts.txt --genecounts unspliced.bus
bustools count -o spliced -g ./tr2g.tsv -e matrix.ec -t transcripts.txt --genecounts spliced.busPreprocessing
Remove empty droplets
Now we have the spliced and unspliced matrices to be read into R:
d <- "./output/neuron10k_velocity"
c(spliced, unspliced) %<-% read_velocity_output(spliced_dir = d,
spliced_name = "spliced",
unspliced_dir = d,
unspliced_name = "unspliced")The %<-% from zeallot unpacks a list of 2 into 2 separate objects in the Python and Matlab manner. How many UMIs are from unspliced transcripts?
sum(unspliced@x) / (sum(unspliced@x) + sum(spliced@x))[1] 0.4114184In previous versions of this notebook, there were more unspliced counts than spliced counts. As part of an ongoing project, I converted the supposedly unspliced bus output into text and inspected it in R as a data frame. The output was wrong; there were still reads mapped to exclusively exonic regions in that bus file. However, the problem was fixed when I made sure that all transcripts in the capture list are also in the transcript list in the kallisto bus output, so the current version should be correct. However, this is still a higher proportion of unspliced counts. In contrast, for velocyto, the unspliced count is usually between 10% and 20% of the sum of spliced and unspliced. Perhaps this is because kallisto | bus counts reads that are partially intronic and partially exonic as unspliced while velocyto throws away many reads (see this GitHub issue).
We expect around 10,000 cells. There are over 10 times more barcodes here, since most barcodes are from empty droplets. The number of genes does not seem too outrageous.
dim(spliced)[1] 55487 1134440dim(unspliced)[1] 55487 723864Most barcodes only have 0 or 1 UMIs detected.
tot_count <- Matrix::colSums(spliced)
summary(tot_count) Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
0.00 1.00 1.00 61.86 2.00 43938.00 A commonly used method to estimate the number of empty droplets is barcode ranking knee and inflection points, as those are often assumed to represent transition between two components of a distribution. While more sophisticated methods exist (e.g. see emptyDrops in DropletUtils), for simplicity, we will use the barcode ranking method here. However, whichever way we go, we don’t have the ground truth. The spliced matrix is used for filtering, though both matrices have similar inflection points.
bc_rank <- barcodeRanks(spliced)
bc_uns <- barcodeRanks(unspliced)Here the knee plot is transposed, because this is more generalizable to multi-modal data, such that those with not only RNA-seq but also abundance of cell surface markers. In that case, we can plot number of UMIs on the x axis, number of cell surface protein tags on the y axis, and barcode rank based on both UMI and protein tag counts on the z axis; it makes more sense to make barcode rank the dependent variable. See this blog post by Lior Pachter for a more detailed explanation.
#' Knee plot for filtering empty droplets
#'
#' Visualizes the inflection point to filter empty droplets. This function plots
#' different datasets with a different color. Facets can be added after calling
#' this function with `facet_*` functions.
#'
#' @param bc_ranks A named list of output from `DropletUtil::barcodeRanks`.
#' @return A ggplot2 object.
#' @importFrom tibble tibble
#' @importFrom purrr map map_dbl
#' @importFrom dplyr distinct
#' @importFrom ggplot2 geom_line geom_hline geom_vline scale_x_log10 scale_y_log10
#' @importFrom tidyr unnest
#' @export
knee_plot <- function(bc_ranks) {
# purrr pluck shorthand doesn't work on S4Vector DataFrame
knee_plt <- tibble(rank = map(bc_ranks, ~ .x[["rank"]]),
total = map(bc_ranks, ~ .x[["total"]]),
dataset = names(bc_ranks)) %>%
unnest(cols = c(rank, total)) %>%
distinct() %>%
dplyr::filter(total > 0)
annot <- tibble(inflection = map_dbl(bc_ranks, ~ metadata(.x)[["inflection"]]),
rank_cutoff = map_dbl(bc_ranks,
~ max(.x$rank[.x$total >
metadata(.x)[["inflection"]]])),
dataset = names(bc_ranks))
p <- ggplot(knee_plt, aes(rank, total, color = dataset)) +
geom_line() +
geom_hline(aes(yintercept = inflection, color = dataset),
data = annot, linetype = 2) +
geom_vline(aes(xintercept = rank_cutoff, color = dataset),
data = annot, linetype = 2) +
scale_x_log10() +
scale_y_log10() +
labs(x = "Rank", y = "Total UMIs")
return(p)
}knee_plot(list(spliced = bc_rank, unspliced = bc_uns)) +
coord_flip()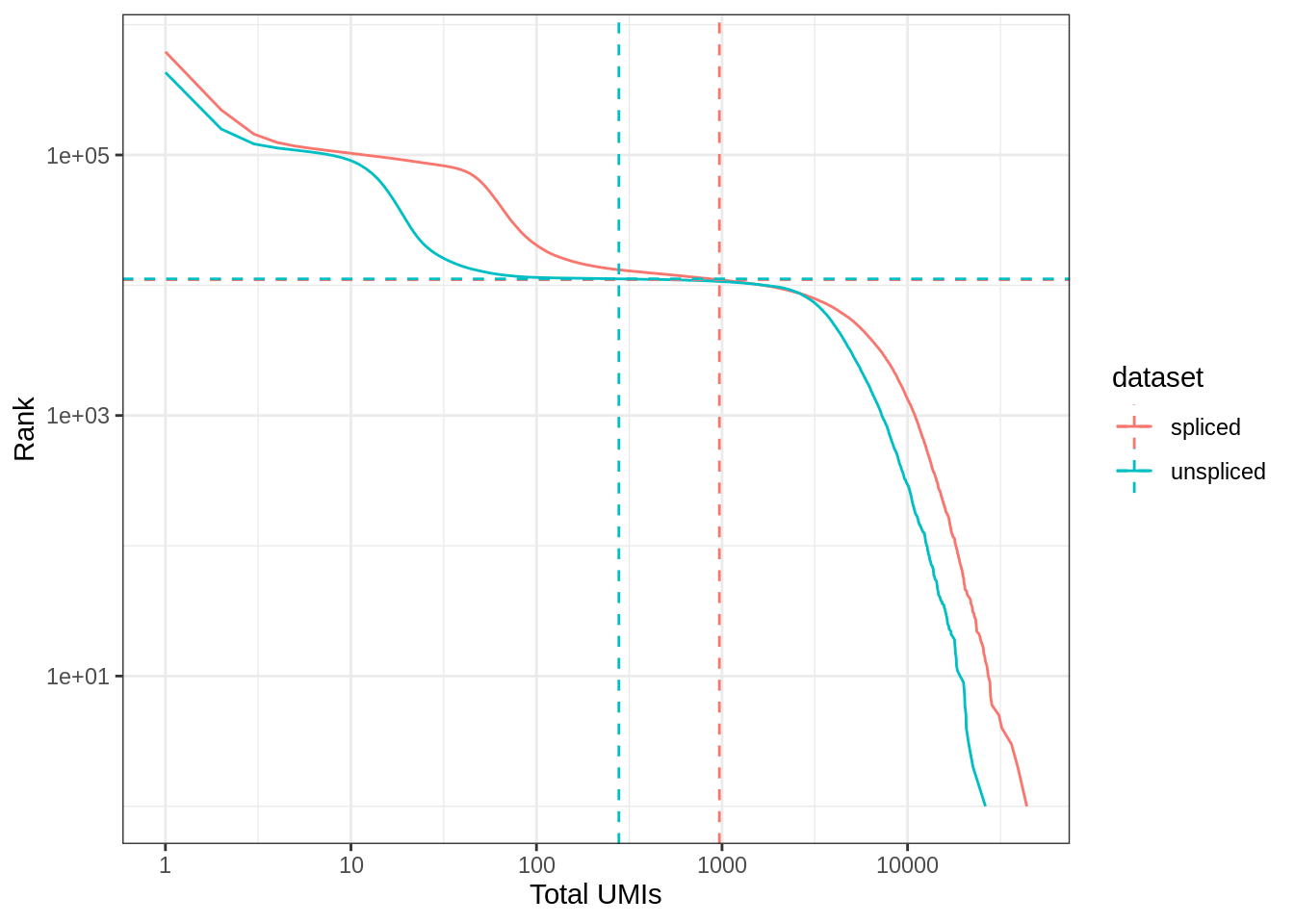
Which inflection point should be used to remove what are supposed to be empty droplets? The one of the spliced matrix or the unspliced matrix?
Actually, spliced and unspliced counts are multimodal data, so why not make one of those promised 3D plots where the barcode rank depends on two variables? The rank (z axis) would now be the number cells with at least x spliced UMIs and y unspliced UMIs. How shall this be computed? The transposed knee plot (or rank-UMI plot) can be thought of as (1 - ECDF(total_UMI))*n_cells. In the ECDF of total UMI counts, the dependent variable is the proportion of cells with at most this number of distinct UMIs. So 1 minus that would mean the proportion of cells with at least this number of distinct UMIs. In the knee plot, the rank is the number of cells with at least this number of distinct UMIs. So dividing by the number of cells, we get 1 - ECDF(total_UMI). Would computing the 2D ECDF be more efficient than this naive approach? There is an R package that can compute bivariate ECDFs called Emcdf, but it uses so much memory that even our server can’t handle. I failed to find implementations of bivariate ECDFs in other languages. There is an algorithm based on range trees that can find multivariate ECDF efficiently.
Before obtaining a more efficient implementation, I used my naive approach that translates this concept into code very literally. Though I used Rcpp, it’s really slow. The trick to make it faster is to only evaluate how many cells have at least x spliced and y unspliced counts at a smaller number of grid points of x and y.
//[[Rcpp::depends(RcppProgress)]]
#include <progress.hpp>
#include <progress_bar.hpp>
#include <Rcpp.h>
using namespace Rcpp;
//[[Rcpp::export]]
NumericMatrix bc_ranks2(NumericVector x, NumericVector y,
NumericVector x_grid, NumericVector y_grid) {
NumericMatrix out(x_grid.size(), y_grid.size());
Progress p(x_grid.size(), true);
for (int i = 0; i < x_grid.size(); i++) {
checkUserInterrupt();
for (int j = 0; j < y_grid.size(); j++) {
out(i,j) = sum((x_grid[i] <= x) & (y_grid[j] <= y));
}
p.increment();
}
return(out);
}As most barcodes have a small number of distinct UMIs detected, the grid should be denser for fewer counts. Making the grid in log space achieves this.
# Can only plot barcodes with both spliced and unspliced counts
bcs_inter <- intersect(colnames(spliced), colnames(unspliced))
s <- colSums(spliced[,bcs_inter])
u <- colSums(unspliced[,bcs_inter])
# Grid points
sr <- sort(unique(exp(round(log(s)*100)/100)))
ur <- sort(unique(exp(round(log(u)*100)/100)))# Run naive approach
bc2 <- bc_ranks2(s, u, sr, ur)What would the “rank” look like?
# can't turn color to lot scale unless log values are plotted
z_use <- log10(bc2)
z_use[is.infinite(z_use)] <- NA
plot_ly(x = sr, y = ur, z = z_use) %>% add_surface() %>%
layout(scene = list(xaxis = list(title = "Total spliced UMIs", type = "log"),
yaxis = list(title = "Total unspliced UMIs", type = "log"),
zaxis = list(title = "Rank (log10)")))